
Table of Contents
Computer fundamentals notes
Hello friends, in this article I have provided computer fundamentals notes on many important topics which are very important for general awareness as well as for examination purpose.
Todays world is a computer world where Computer is used almost in every field ranging from education, health, finance, sport etc. In this situation it becomes very essential for us to learn computer fundamentals so that we do not find any difficulty in operating computer.
In this article on computer fundamentals notes I have explained the topics from the very begining which will be very helpful for the beginners. I have made every effort to explain in a simple and easy way so that you can understand.
I am going to upload very soon a free downloadable PDF file on computer fundamentals in this page which you will be able to download it from here. So keep visiting this page.
Let’s start reading the topics now.
origin of the word ‘computer’
The word ‘computer’ is originated from a Latin word ‘computare’ in which ‘com’ means to put together and ‘putare’ means to think and to prune . So computer means to sum up, to calculate.
Definition of a computer
More precisely a computer can be defined as a machine which performs computations. It is a machine which accepts raw data from the user as an input, processes it and converts it into meaningful information. It works on the data according to the instruction given by the user and produces correct result or output and displays it to the user.
A computer is made up of various devices such as input devices, output devices, processing devices, storage devices which help in entire process of computation.
Following diagram shows a computer system

Components of a computer
A computer system has mainly three components
i. Input unit
ii. Processing unit
processing unit is again divided into three sections
a. ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit)
b. CU (Control Unit)
c. MU (Memory Unit)
iii. Output unit
Following diagram shows the basic components of a computer
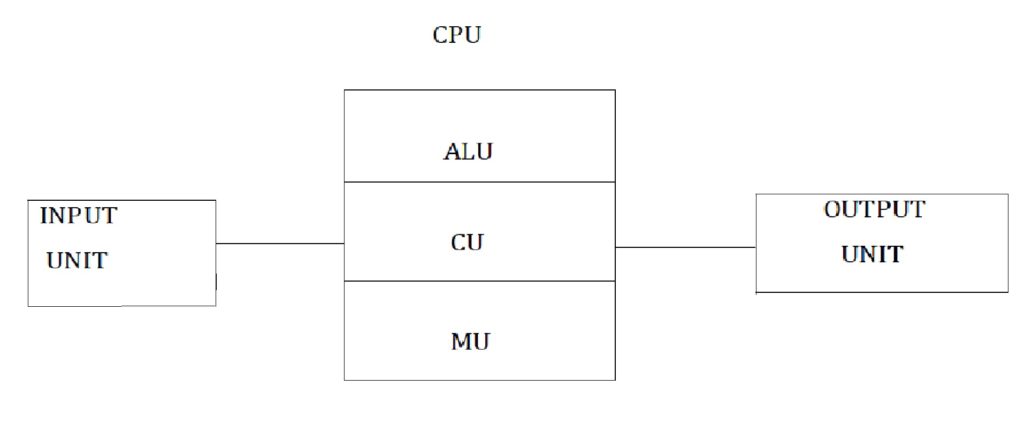
Input unit
The input unit consists of all the input devices that can be connected to a computer. It helps a user to enter data and instructions into a computer in the form of text, image, audio or video.
The various example of input devices are Mouse, Keyboard, Scanner, Microphone, Trackball, Joystick, Lightpen, Touchscreen etc.
we can enter information into a computer by clicking buttons on the Mouse.
keyboard is used to enter data and instruction into a computer by pressing the keys available on the keyboard.
We use Scanner to take a scanned image of a hard copy to enter it into a computer.
Microphone is used to take audio input for a computer. We can do voice recording with it which we can use as an input for a Computer.
We can use Trackball instead of a Mouse when we do not have sufficient space to keep the Mouse .
Processing unit
The processing unit of a computer is the CPU. It is called the brain of a computer system. It consists of three sections
a. ALU
b. CU
c. MU
ALU
ALU stands for Arithmetic Logic Unit.This is the processing section of a computer. It not only performs arithmetic calculations but also takes logical decisions so it performs both numerical and non numerical operations.
CU
CU stands for Control Unit. It controls the processing of data in a computer. It coordinates the operations of other units in a computer.
When data and instructions are entered through input device, CU sends both data and instructions to the memory of a computer. When any arithmetic /logical operation is to be performed on the data it sends data to the ALU and after processing, it again sends data back to the memory for displaying on output device.
MU
MU stands for Memory Unit. The memory unit of a computer is made of memory chips. It stores data and instructions temporarily before and after they are processed by the CPU.
Output unit
The output unit consists of all the output devices that can be connected to a computer. It helps to display the result or output in the form of soft copy or hard copy.
friends, if you want to know in detail what is a soft copy and hard copy then click the link
The various example of output devices are Monitor, Printer, Plotter, Speaker etc.
Watch my YouTube video on components of a computer for better understanding.
Characteristics of a computer
Following are the characteristics of a computer
1.Speed: A computer works at a very high speed. It gives us the result in a second no matter how complex the calculation is.
2.Accuracy : A computer always gives us accurate results. It never makes any mistakes. If the question is correct, the answer produced by the computer will also be correct.
3.Diligence: A computer never gets tired. It does not get bored of doing the same work over and over again even if it has to do the same work million times, it does giving 100 Percent correct result.
4.Versatility: A computer is very versatile. It can perform a series of different tasks one after another.
5.Storage capacity: A computer can store a large amount of data in its memory and the data stored in it can be retrieved whenever it is needed.
Functions of a computer
A computer performs the following functions
i.Input: It takes raw data from the user to process on it. So input is the first task/function of a Computer.
ii.Process: It processes the data after accepting /taking data from the user . The processing of data takes place in the CPU of a Computer. So processing of data is the second task/function of a Computer.
iii.Output: After processing of data, it produces result /output. So producing result or output is the third task/function of a Computer.
iv. store: Computer also stores data in its memory which can be retrieved whenever it is needed.
Generations of computer
The following table summarises the various generations of computer
| Sl. No. | Generations | Periods | Hardware Technology used |
| 1 | First Generations | 1940s-1950s | Vacuum Tubes |
| 2 | Second Generations | 1950s-1960s | Transistors |
| 3 | Third Generations | 1960s-1970s | Integrated Circuits |
| 4 | Fourth Generations | 1970s-1980s | Microprocessors |
| 5 | Fifth Generations | 1980s-till date | Artificial Intelligence |
Friends, if you are interested to study Generations of computer in detail click the link below
Advantages and Disadvantages of a computer
Below given are some of the advantages and disadvantages of a computer –
Advantages of a computer
Following are some of the advantages of a computer –
i. Speed: A computer works very fast on the data. It acts on the data entered by the user and gives us result very fast.
ii. Accuracy: A computer always provides us correct result. If the data and the instructions entered by the user are correct , the result produced by a computer is also correct. It never makes any mistake unlike human being.
iii. Diligency: A computer never gets tired or bored of doing the same task again and again.
iv. Versatility: A computer can perform a series of different tasks simultaneously unlike human being.
v. Storage: A computer can store a large amount of data in its memory from where data can be retrieved anytime.
Disadvantages of a computer
Some of the disadvantages of a computer are as follows-
i. No intelligence: A computer does not have any intelligence. It can not think of its own. It acts on the data according to the instructions given to it.
ii. Depends on electricity: A computer can not run without electricity. It stops working when the power supply is interrupted or the charge in the battery is exhausted.
iii. Hardware failure: The entire computer system crashes when any of the hardware failure occurs. This is another disadvantage of a computer.
iv. Security hazard: A computer is prone to attacks by hackers, viruses, etc. which is another disadvantage of a computer.
v. Communication problem: A computer does not understand high level language or human language. It understands only machine language i.e. binary language which consists of only 0s and 1s which we human being also can not understand.
Uses of a computer
Now a days computers are used in many different fields.
Following are some of the fields where computers are used extensively
- Education: Now a days computer has become an important part in education system. Computers are used in schools, colleges, elearning platforms for providing education to students. Computers are used to teach students on different topics in a classroom, to maintain records of students, to provide online teaching, to take online test for students etc.
- Sports: In sports computers are used many purposes. In cricket match sometimes the first umpire and second umpire are not able to take correct decision, in that case the third umpire’s help is taken who takes the correct decision watching the recording of the match on computer. The sportsman also practice and improve their skills with the help of simulation software on computer.
- Banks: Almost every bank now a days uses computer to keep records of their customers, to keep the details of money transactions and also to keep their financial documents safely.
- Business : Computer has become an integral part in corporate sector. Here computers are used to store record of all the business transactions. Now a days, we find computers in every shopping malls, supermarkets, offices etc. We can buy and sell things online, pay bills online, book tickets etc. The popularity of computer is rapidly increasing day by day in business fields.
- Communication: Computers play a major role in the field of communication. Now a days we can communicate with persons , groups through chat, emails over internet. Internet helps us to find information on every topic. It is the easiest and fastest way of communication. Computer network helps the user to access files located in remote servers.
Branches of a computer
There are two branches of a Computer
i. Software
ii.Hardware
Hardware
These are the physical components of a Computer which we can touch and feel i.e. the tangible parts of a Computer are called Hardware. These are the peripheral devices which help a computer to perform computations.
For example, Monitor, CPU, Keyboard, Mouse , Printer, Scanner etc.
Software
Software is a group of programs which are used to carry out specific tasks in a Computer.It tells the Computer what to do and how to do the tasks. There are two types of software
i. Application software
ii.System Software
APPLICATION SOFTWARE
Application software helps to perform a specific task in a specific field in a Computer system. For example, DBMS softwares, Image editing softwares, Video editing softwares, Text editing softwares, Accountancy softwares etc.
we use DBMS softwares such as MS Access, Oracle, MySQL etc.to create databases ,tables, forms, reports.
Image editing softwares such as Photoshop, CorelDraw etc. to edit images.
Text editing softwares such as MS Word, Notepad, Wordpad, Google docs etc. to create and edit text documents
and we use Spreadsheet softwares such as MS Excel, Calc etc. to perform mathematical calculations
SYSTEM SOFTWARE
System software helps in smooth functioning of a computer system. A computer system cannot run without a system software.
The operating system installed in a Computer system is an example of System software.
Memory in a computer
The memory in a computer stores data and instructions entered by a user. The memory of a computer is divided into two categories
i. Primary memory
ii. Secondary memory
Primary Memory
Primary memory is also called internal memory as it is located inside the computer.The primary or internal memory is divided into many storage locations each of which can hold data and instructions. The primary memory is also known as Main memory.
The Internal or Primary or Main memory is again classified into two categories
i. RAM
ii.ROM
RAM
RAM stands for Random Access Memory. It is also called Read/write memory as we can read and write on it. The data and instructions entered through input device are temporarily stored in RAM during processing in a computer. The contents of this memory are lost when the computer is switched off or the power supply is stopped . That is why RAM is called volatile or temporary memory.
RAM can be classified into two categories
i. Static RAM
ii. Dynamic RAM
ROM
ROM stands for Read Only Memory. It is called so as we can only read from it but cannot write or change its contents. ROM is called non volatile or permanent memory. The contents of this memory are written by the manufacturer for running of the computer. These are basically the starting programs.
ROM can be classified into three categories
i. PROM
ii. EPROM
iii. EEPROM
PROM
PROM stands for Programmable Read Only Memory. It can be programmed or written only once after manufacturing of a computer. The writing process in PROM is performed electrically with a special equipment. PROM is more flexible and convenient to use than ROM. PROM is also volatile or permament like ROM.
EPROM
EPROM stands for Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory. EPROM can also be read and written like PROM but the writing process in EPROM is not as simple as ROM/PROM. The data in EPROM can be erased by exposing the chip to ultra violet light. It is costly to use. One disadvantage in EPROM is that data of a particular memory location can not be erased.
EEPROM
EEPROM stands for Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory. This type of ROM can be programmed electrically as many times as we want. The advantage of EEPROM over EPROM is that data of a particular memory location can be erased in it.
Secondary Memory
Another type of memory is secondary memory or external memory. It is called external as it is located outside the CPU. The data and instructions are stored permanently in secondary memory and can be retrieved whenever needed. The CPU can not process the data directly in secondary memory, it must be brought to RAM of a computer for processing.
The following chart shows the classification of memory
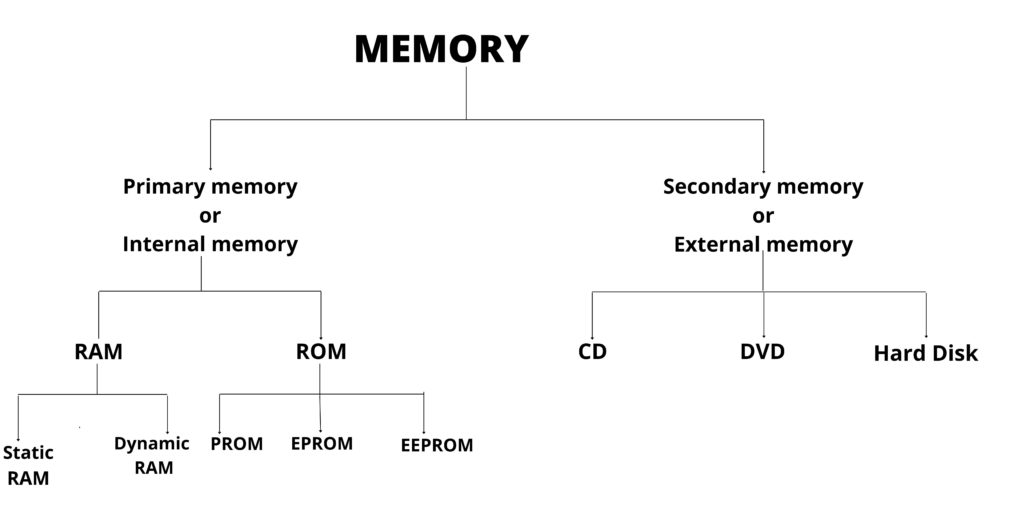
Memory units
The data that is stored in memory of a computer is internally represented in the form of 0s and 1s. Each of these 0s and 1s is called as BIT.
Following are the various units used for measurement of computer memory
i. BIT : BIT stands for Binary Digit. It is the smallest unit of information that a computer handles.
ii. Nibble: Nibble is the second smallest unit of information for measuring memory capacity. A combination of 4 bits make one Nibble.
iii. Byte: A Byte is a combination of eight bits arranged in a particular sequence.
iv. Kilobyte: A combination of 1024 bytes is called as one Kilobyte.
v. Megabyte: A combination of 1024 Kilobytes is called as one Megabyte.
vi. Gigabyte: One Gigabyte is equal to 1024 Megabytes.
vii. Terabyte: One Terabyte consists of 1024 Gigabytes.
Operating System
An operating system is an essential component of a computer system. It is a large collection of software which manages resources of the computer system such as memory, process, files, input and output devices. It provides us an interface that enables us to interact with the hardware of a computer.
The primary objective of an operating system is to make computer convenient to use and utilise computer hardware in an efficient manner.
The various examples of operating system are Linux, Unix, Windows 98, Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Android, Apple etc.
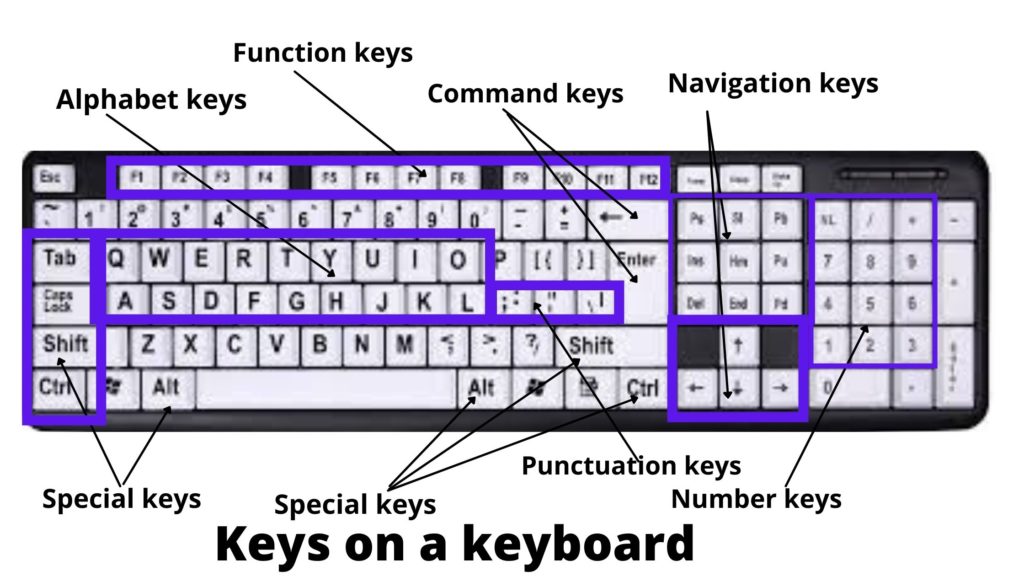
Types of keys on a keyboard
Following are the types of keys available on a keyboard –
- Alphabet keys such as A B C…………………………………Z
- Number keys such as 1 2 3 4 ……………………………..9
- Function keys such as f1 f2 f3……………………………..f12
- Special keys such as ctrl, caps lock, shift, tab, alt etc.
- Command keys such as insert, enter, backspace, delete etc.
- Navigation keys such as pgup,pgdown, home, end, arrows(left, right, up, down) etc.
- Symbol keys such as @, !, #,$,%, ^,&,* etc.
- punctuation keys such as : , ; . ‘ ” ? !
Types of computer
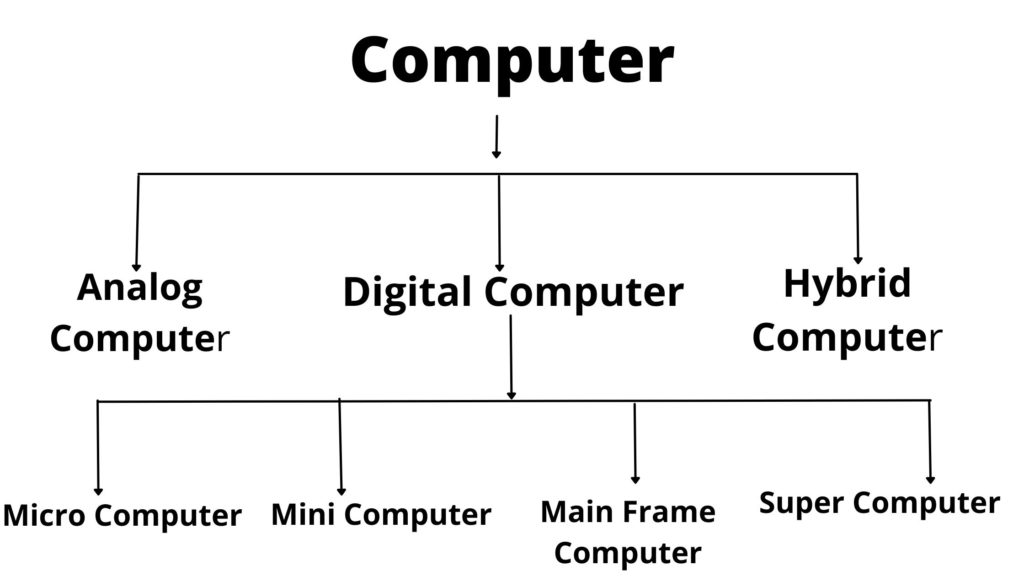
Computers are mainly divided into three types
- Analog Computer
- Digital Computer
- Hybrid Computer
Analog Computer
Analog computer is a computer which works on continuous signals. This type of computer always gives approximate result. It does not provide exact result. Analog computers are used in scientific calculation.
Examples of Analog computers are Stethoscope, Analog thermometer etc.
Digital Computer
Digital computer works on digitals signals i.e. 0s and 1s. It always produces accurate result. Digital computers are used in offices, educational institutions, banks, companies etc.
Examples of digital computers are digital watch, Digital thermometer, calculator etc.
Depending on the size, power and processing speed Digital computer is again classified into four categories such as
- Micro computer
2. Mini computer
3. Main frame computer
4. Super computer
Micro computer
Micro computer is the smallest of all the types of computer. Inside a Micro computer, Arithmetic Logic Unit and Control Unit are combined on a single chip called a Micro Processor. Micro computer contains two types of memory RAM and ROM.
Peripherals such as Keyboard and Visual Display Unit(VDU) are parts of a Micro Computer. A Micro Computer is also known as Personal Computer.
Micro computers are used as home computers by family or as personal computers by business professional or small business houses where volumes of data processing and speed requirements are less.
Desktop computer, laptop, Notebook computer, Tablet, palmtop etc. are examples of Micro computer.
Mini computer
Mini computers are more powerful than Micro computers. It support several users. It has larger RAM and backing storage. It can process data more quickly than Micro computer.
Mini computers are used by medium sized organization for application like Payrolls and financial accounts etc. It can also be used for system like reservation and banking etc.
The first popular Mini computer is PDP -8.
Main Frame computer
Main Frame computers are very large and powerful computers. They can process large amount of data very quickly. These types of computers are used by big companies. They can be linked into a network with smaller departmental Micro computers or with each other.
Main Frame computers are used for payroll computations, Airline seat reservation, engineering applications etc.
Super computer
Super computers are the most powerful of all the types. Super computers have multiple processors and All the processors perform simultaneously for different tasks.
Super computers are used for complex scientific applications such as Rocket launching, weather forecasting, testing of nuclear weapons etc.
Hybrid Computer
hybrid computer uses both analog and digital signals simultaneously. Hybrid computers are used in hospitals
Examples of hybrid computers are Echo cardiogram machine, fuel dispensing machine etc.
The diagram on the types of computer
The diagram given below shows the classification of computer
Computer Network
When a group of computers and associated devices are connected to each other for sharing files and resources is called computer network.
A typical computer network consists of the following
- Server
- Workstation
- Communication channel
Server: Server is the central computer which provides services to other computers like files, access of the peripheral devices connected in the network.
Workstation: Workstation is any computer which access files and peripheral devices connected to the network.
Communication channel: communication channel is the path or the link through which the computers and peripheral devices are connected.
Types of computer network
Computer Network is of following types,
- PAN (Personal Area Network)
- LAN (Local Area Network)
- MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
- WAN (Wide Area Network)
PAN : PAN is restricted to very small area such as rooms in a house . It can be a network established among various devices present in the house such as Laptop, Desktop computer, smartphone, printer etc.
LAN : LAN covers a small geographical area such as a building , campus etc.
MAN : MAN covers area such as in a metro city.
WAN: WAN is the largest network of all the networks. It covers worldwide. Internet is an example of WAN.
Internet
Internet is a collection of interconnected networks for sharing information worldwide. It is an international network. It is the largest network of all the networks. Internet connects many commercial, government and educational networks as well as individual computers. It offers a range of services to its users such as file transfers between internet users, communication among internet users through emails, availability of information on various fields etc.
Intranet
Many organizations use a special type of network to communicate and share information among themselves in the organization. Such network is known as Intranet. Unlike Internet this network is accessible only to the authorized users of the organization. Intranet is not a big network like Internet.
Computer fundamentals FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Who is known as the father of computer ?
Ans: Charles Babbage
Which is the first Digital computer ?
Ans: UNIVAC
Who invented Difference Engine ?
Ans: Charles Babbage
Which is called the brain of a computer ?
Ans: CPU
What is another name for monitor in computer ?
Ans: VDU (Visual Display Unit )
What is the full form of COMPUTER ?
Ans: Commonly Operated Machine Particularly Used in Technology Education and Research.
Which is the first Super computer developed in India ?
Ans: PARAM 8000
How many Generations of computer are there ?
Ans: There are 5 Generations of computer.
Conclusion
Friends, I hope after reading the above article you must have clear concept on various topics on computer fundamentals. If you have any question or doubt regarding this please feel free to comment in the comment section or email me at [email protected].
If you like the contents please share with your friends so that they can also have knowledge on it.
Friends, if you are interested to read various questions on computer fundamentals for competitive examinations, click the link MCQs on computer fundamentals.
Recent posts
- Download PDF of Class X Information Technology (IT) Code 402 NCERT Book, Syllabus and Previous Year Question Papers
- Information Technology (IT) code 402 and 802 |Class IX | Class X| Class XI| Class XII| NCERT book, syllabus and previous year question paper download PDF under CBSE
- Class IX Employability Skills Unit 5 : Green Skills Exercise and Additional Questions Answers under SEBA
- Class IX IT Domestic Data Entry Operator book unit 5: Digital Presentation questions answers under SEBA
- Class IX IT/ITeS Domestic Data Entry Operator questions answers under SEBA
Read more
- Notes on history of computer
- Notes on generation of computer
- Notes on MS Windows
- Notes on cyber Security
- MCQ on history and generation of computer
- Quiz on history and generation of computer
- MCQ on computer fundamentals

Hello students,
Welcome to my site. I am the founder of the blog elearnersmentor.com. I have been in teaching profession since 2004. Presently I am working as a vocational subject teacher(IT) in a reputed govt. higher secondary school. Read more